
Blockchain Terminology for Beginners
Blockchain is not a new topic, but it is often not understood selectively. There are many myths and misunderstandings about blockchain. The term itself, just like cryptocurrencies, even though it has recently gained a growing number of recipients, is still considered elitist and somewhat mysterious.
5 min read
What is Blockchain, and why is there no future in digitization without a better understanding of it?
Definition of Blockchain
To start from basics. Definition of a Blockchain is a distributed database that is shared by the nodes of a computer network. As a database, the blockchain stores information electronically in a digital format. Blockchains are best known for their crucial role in cryptocurrency systems, such as Bitcoin, maintaining a secure and decentralized record of transactions. Blockchain innovation is that it guarantees the fidelity and security of the data record and generates trust without the need for a trusted third party.
Virtually anything of value can be tracked and sold on the blockchain network, reducing risk, and lowering costs for all involved. Doing business, regardless of sector, relies on sharing information. The faster and more efficiently this is done, the better for business.
Blockchain is ideal for information delivery because it provides instant, shared and completely transparent stored information that authorized individuals can only access. A blockchain network can track orders, payments, bills, production, etc. The tracking of information is done in a way that is not hidden and clear to everyone with access, so everyone who has permission is fully informed and has insight into the information.
How does blockchain work?
The most crucial element of blockchain technology is the transaction, which is the act of transferring some digital value from one address to another. But it is important to remember that inside the block, many transactions or non-transaction can occur. Every situation is possible in Blockchain.
- Each transaction takes place inside the “block” of data. These transactions show the movement of assets. They can be tangible (product) or intangible (intellectual). A block of data can record information of your choice: who, what, when, where, how much, etc.
- Each block is connected These blocks form a data chain when a resource moves from place to place, or the owner changes hands. Blocks confirm the exact time and sequence of transactions, and blocks link together securely to prevent any block from changing or inserting a block between two existing blocks.
- Transactions are blocked together in an irreversible chain: the blockchain. The purpose of blockchain is to allow digital information to be recorded and distributed but not edited. Blockchain is the basis for immutable ledgers or records of transactions that cannot be altered, deleted, or destroyed. Blockchains are also known as distributed ledger technology (DLT).
How does it work?
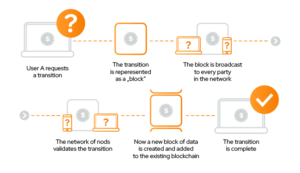
Each additional block strengthens the verification of the previous block and thus the entire blockchain. This makes the blockchain visible, providing the necessary power of immutability. This eliminates the possibility of tampering by a malicious actor – and creates a record of transactions that you and other network members can trust.
It’s worth noting that a regular database typically arranges its data into tables, whereas a blockchain, as its name suggests, agrees its data into chunks (blocks) that are linked together. This data structure inherently creates an irreversible data timeline when implemented in a decentralized manner. When a block is populated, it is embedded and becomes part of this timeline. Each block receives an exact time signature when it is added to the chain.
It is also worth mentioning at this time about smart contracts. It is a computer program or protocol designed to digitize contracts, automatically verify them, enforce negotiations, or document legally significant events by the terms of these contracts. Smart Contract is the next step in progress made in blockchain technology.
Blockchain and Bitcoin.
In the case of Bitcoin, blockchain is used in a decentralized manner so that no one person or group has control – instead, all users collectively retain control. To understand the relationship between cryptocurrency and blockchain, we must first understand the idea of this first one.
The Bitcoin protocol is built on the blockchain. In a research paper introducing the digital currency, the pseudonymous creator of Bitcoin, Satoshi Nakamoto, described it as:
a new electronic cash system that’s fully peer-to-peer, with no trusted third party.
The key thing to understand is that Bitcoin uses blockchain only to record a ledger of payments transparently. In the case of Bitcoin, this means that transactions are permanently recorded and visible to everyone.
What are Blockchain networks, and how can they be used in different sectors?
There are several ways to build a blockchain network. They can be public, private, or created by a consortium.
Blockchain for Industry / Supply Chain The food industry is increasingly using blockchain to track the path and safety of food from farm to user.
Healthcare Healthcare providers can use blockchain to store their patients‘ medical records securely.
Oil and gas Oil and gas are traded commodities, and trade finance is a massive challenge for the commodity trading market. Using blockchain-based solutions enables the issuance of letters of credit and trade financing while ensuring complete transparency of the actions of the various parties to the transaction.
Financial services Thanks to blockchain, banks can also exchange funds between institutions in a faster and more secure way, and consumers can see how their transactions are processed.
And other sectors such as transportation, heavy industry, etc.
Is Bitcoin secure?
Blockchain technology provides decentralized security and trust in several ways but how about Bitcoin. Is crypto secure and how does it influence trust in Blockchain?
Although the confidentiality of the blockchain network protects users from intrusion and protects privacy, it is also sometimes associated, partly rightly, with illegal trade and activity on the web. An example of using Blockchain for illegal transactions is the case of Silk Road, an online marketplace for drugs and dirty money laundering that the FBI shut down in 2013. Since then, much has changed in the operation of cryptocurrencies and this market. Black clouds and bad PR are leaving this technology, but it is still a long way from being considered entirely trustworthy by the public.
Energy costs.
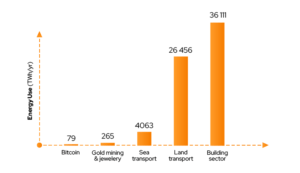
The cost of technology is also a hot topic. When it comes to energy usage compared to what Bitcoin gives, for example, here, the energy usage is relatively shallow – this is bitcoin’s advantage – there is a massive amount of $$ processed through it every second with low network maintenance.
The table below shows energy consumption in different sectors. As you can see, the opinions about its consumption by the cryptocurrency market are not exactly accurate.
Summary
So, what does the future of Blockchain be like? At the end of 2021, the global Blockchain technology market size was $5.92 billion and is estimated to reach $10.02 billion by 2022. North America dominated the global Blockchain technology market in 2021 with a market share of 37.95%. This is just the beginning. Experts indicate that its most significant growth is still ahead, and all predictions of further growth will be more than sure. It is worth keeping a close eye on Blockchain in your business sector so as not to miss the opportunity for the development of your company.




